- The static friction (The biggest type of eve),
- Sliding,
- rolling,
- liquid and gas.





Welcome to AISZ's 7th Grade Science Blog. Here you will find information about what we are learning in class at the moment and other random thoughts we have. Enjoy our posts and feel free to leave us a comment or two.





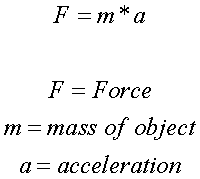 Hello everyone who reads my post!!!
Hello everyone who reads my post!!!
Today in our science class we talked about force, different types of force, gravity, spring scales, a little bit about friction, and that’s mostly it!
So, first, we watched three short videos about the things I listed (force, gravity). The first video was a man driving a car, this video showed us a few graphs and talked about acceleration. The second video was about a brave person, jumping from a very big height, from the top of the bridge. This video talks about the gravity. And the third video showed us some bicyclist, this video talked about the friction.
The links that might help you learn:
http://www.brightstorm.com/science/physics/newtons-laws-of-motion/law-of-force-and-acceleration-newtons-second-law-of-motion
http://www.edinformatics.com/math_science/force.htm
http://www.asknumbers.com/WhatisForce.aspx
http://www.racemath.info/motionandenergy/What_is_Acceleration.htm
http://www.theory.caltech.edu/people/patricia/gravtop.html
http://zagreb.ceesa.net/course/view.php?id=188
I HOPE YOU LIKED MY POST! ! ! AND THE NEXT SCRIBE IS… (NO DRUM ROLL) MARIA CHIARA!


